SCME: Single Center Multipole Expansion

A transferable and efficient polarizable interaction potential for extremely accurate solvent simulations in QM/MM systems.
About SCME
For a interaction potential function to be transferable, polarizability needs to be included, i.e., the effect of distortions to the electron cloud of the molecules. A systematic way of developing a transferable potential function can be based on a well-defined multipole analysis of electrostatics.
In the case of 𝐻2𝑂 and 𝐶𝐻3𝐶𝑁, the entire electron distribution can be represented approximately by considering the lowest moments up to the hexadecapole. Moreover, including the effects of polarizability through induced moments helps to model the properties of the molecule
in the presence of an external field. The single-center multipole expansion (SCME) method for describing molecular interactions developed by the EOJ group, evades the use of point charges (which re-
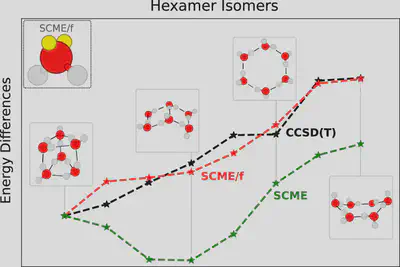
quires computational demanding Ewald summation to converge) by performing multipole analysis on the molecule as a whole, rather than including a separate multipole expansion for each atom. The group has pioneered the method and developed transferable SCME potentials for modeling pure water(SCME-𝐻2𝑂) and pure acetonitrile (SCME-𝐶𝐻3𝐶𝑁).
For more information visit the SCME documentation.